Measuring energy consumption accurately is essential across various sectors, from industrial facilities to residential homes. DIN rail power meters offer a compact and efficient solution for this need. This article will explore what these meters are, why they're important, their different types, how to choose the right one, and provide guidance on installation and wiring.
What is a DIN Rail Power Meter?
A DIN rail mounted energy meter is a compact device designed to measure electrical energy consumption and is specifically engineered to be mounted on a standard DIN rail within an electrical enclosure or distribution board. These meters are widely used for their space-saving design and ease of integration into existing electrical systems.
The primary purpose of a DIN rail power meter is to accurately measure and display electrical parameters such as voltage, current, power, and energy consumption (kWh). They are crucial for:
- Cost Allocation: Accurately billing tenants or departments based on their actual energy usage.
- Energy Management: Identifying areas of high consumption, optimizing energy efficiency, and reducing operational costs.
- System Monitoring: Keeping track of electrical load, ensuring system stability, and preventing overloads.
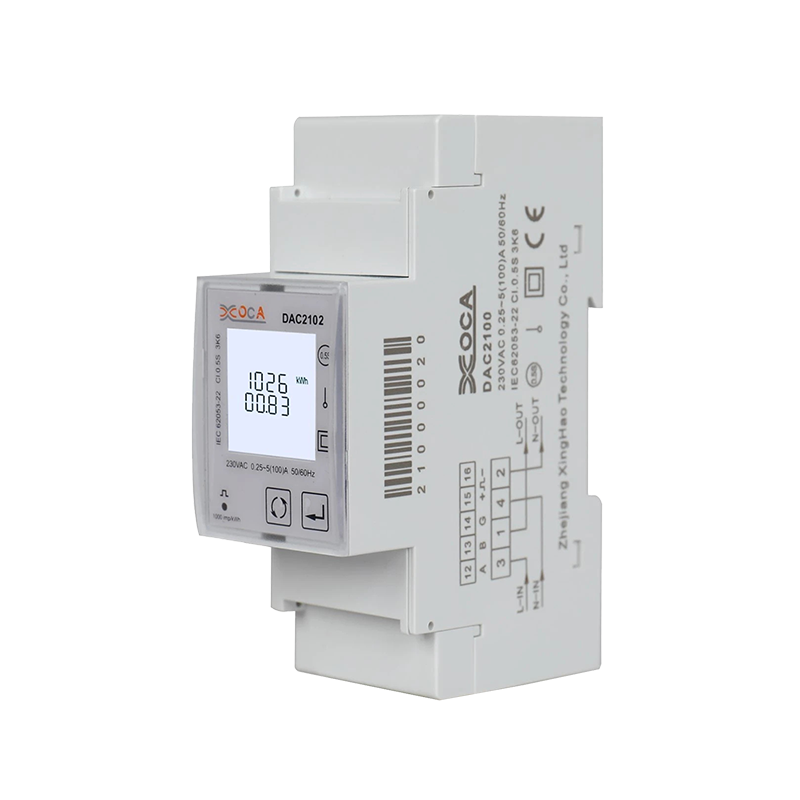
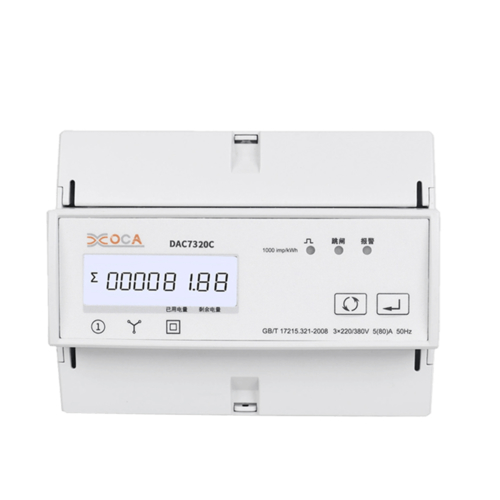
Dac2102 DIN Rail Single Phase Intelligent AC Power Meter
Why Do You Need a DIN Rail Power Meter?
The versatility and compact nature of DIN rail power meters make them indispensable in a variety of applications:
Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, an industrial DIN rail kWh meter is vital for monitoring the energy consumption of machinery, production lines, or specific departments. This allows businesses to:
- Track energy usage per product or process.
- Implement energy-saving initiatives.
- Optimize peak demand charges.
Commercial Applications
Commercial buildings, such as offices, retail spaces, and data centers, often utilize these meters for sub-metering. This enables precise billing for individual units or tenants and helps in managing overall building energy consumption.
Residential Applications
For homeowners, a DIN rail meter for home energy monitoring provides insights into household electricity usage. It can help in:
- Identifying energy-hungry appliances.
- Understanding consumption patterns to reduce electricity bills.
- Monitoring specific circuits like those for electric vehicle charging or heating systems.
Main Types of DIN Rail Power Meters
DIN rail power meters come in various configurations to suit different electrical systems and monitoring needs.
Single Phase vs. Three Phase DIN Rail Power Meter
The choice between single-phase and three-phase meters depends on your electrical supply:
- Single Phase DIN Rail kWh Meter: These meters are designed for single-phase electrical systems, commonly found in residential homes and small commercial establishments. They measure voltage and current on a single live wire and a neutral wire.
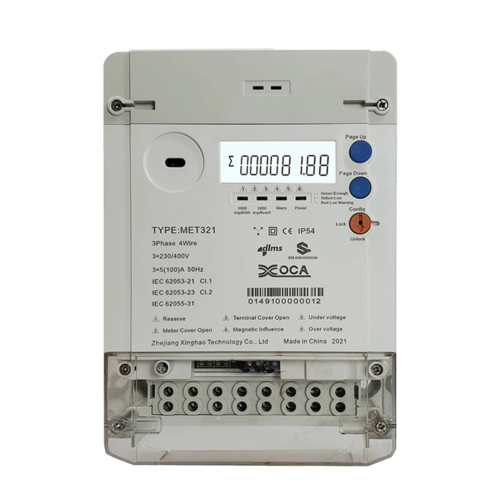
- 3 Phase DIN Rail Power Meter: These are used in three-phase electrical systems, prevalent in industrial facilities and larger commercial buildings. They measure power and energy across three live wires, often with or without a neutral wire, providing a comprehensive view of consumption in complex setups.
Smart Meter vs. Traditional Meter
Advancements in technology have led to the development of smart DIN rail power meter options:
- Smart Meters: These meters offer advanced functionalities beyond basic energy measurement. They typically include features like remote monitoring, data logging, time-of-use metering, and sometimes even power quality analysis (e.g., harmonic distortion). They enable proactive energy management and integration with building management systems.
- Traditional Meters: These are more basic, providing real-time readings on a display but lacking advanced communication or data storage capabilities.
Communication Protocol Support
Many modern DIN rail power meters support various communication protocols, allowing for integration into larger monitoring networks:
- DIN Rail Energy Meter with RS485: RS485 is a common serial communication standard used for long-distance data transmission in industrial environments.
- Modbus DIN Rail Power Meter: Modbus is a widely adopted communication protocol for industrial electronic devices, facilitating data exchange between meters and control systems.
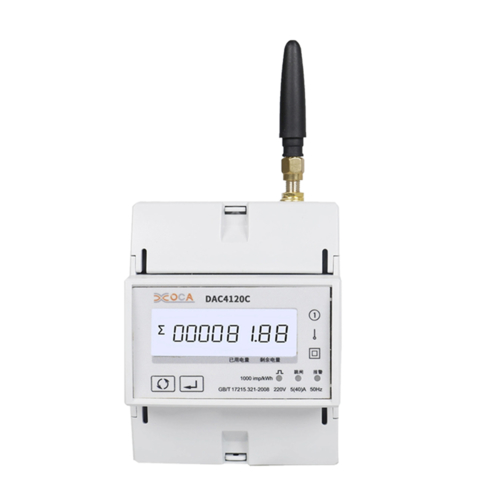
- Wireless DIN Rail Power Meter: Some meters offer Wi-Fi or other wireless communication options, providing flexibility in installation and enabling cloud-based monitoring.
How to Choose the Right DIN Rail Power Meter?
Selecting the appropriate DIN rail power meter requires considering several key factors to ensure it meets your specific requirements.
Key Parameters
- Voltage and Current Range: Ensure the meter's voltage and current ratings match your electrical system's specifications. For high-current applications, you might need a DIN rail power meter with CT clamps (Current Transformers) to accurately measure current indirectly.
- Accuracy Class: Meters are categorized by accuracy classes (e.g., Class 1, Class 0.5). Higher accuracy classes are important for billing purposes or critical energy monitoring.
- Installation Method: Confirm the meter is designed for DIN rail mounting and fits within your available panel space.
Special Function Requirements
Consider any additional features you might need:
- Solar Monitoring: For renewable energy systems, the best DIN rail energy meter for solar applications can monitor both generated and consumed energy, helping optimize self-consumption.
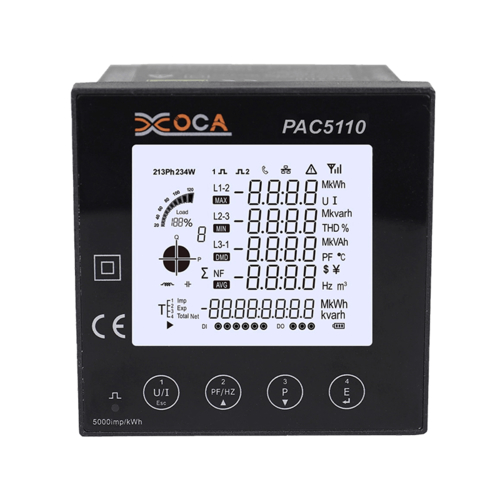
- Harmonic Analysis: Some meters can detect and analyze harmonic distortions in the power supply, which can be critical for maintaining power quality in industrial settings.
- Sub-Metering: If you need to monitor specific circuits or tenants, ensure the meter supports sub-metering capabilities.
Installation and Wiring Guide
Proper installation and wiring are crucial for the accurate and safe operation of your DIN rail power meter.
DIN Rail Installation Steps
DIN rail meters are designed for straightforward installation. Typically, they simply clip onto a standard 35mm DIN rail. Refer to the meter's manual for specific instructions, which often include visual guides or links to video tutorials.
CT (Current Transformer) Wiring Precautions
If your meter requires CT clamps for current measurement, proper wiring is essential. Ensure the CTs are installed in the correct direction (indicated by an arrow on the CT) and connected to the corresponding terminals on the meter. Incorrect wiring can lead to inaccurate readings or damage to the meter.
Communication Module Configuration
For meters with communication capabilities, such as a Modbus DIN rail power meter, configuring the communication settings is necessary. This typically involves setting parameters like the Modbus address, baud rate, and parity in the meter's menu or via software. Refer to the meter's manual for detailed instructions on configuring Modbus RTU/TCP settings.

 English
English 中文简体
中文简体







